-
Kinematics
Kinematics is concerned with describing the way in which objects move.
-
Displacement
An objects total change in position. If a man runs around an oval 400 meter track, stopping at the precise location he began, though he ran a distance of 400 meters, his total displacement was 0.
-
Dynamics
Dynamics focuses on understanding why objects move the way they do.
-
Reference frame
The coordinate system with respect to which motion is being described.
-
Speed
A measure of how fast an object is moving.
-
Average velocity
The time-average of the velocity function over a specified time-interval. (See formula below.)
-
Instantaneous velocity
The value of the velocity function at a particular instant in time. (See formula below.)
-
Gravitational acceleration
The gravitational acceleration of objects near the earth's surface is the same for all objects regardless of mass and is given by the number g = 9.8m/s2.
-
Scalar-valued function
A function that outputs scalars (regular numbers). Most common functions that you are probably familiar with are scalar-valued functions.
-
Vector-valued function
A function that outputs vectors. This means that while the domain of the function may consist of scalars, the values in the range are all vectors.
-
Position function
A position function can be either scalar-valued (for motion in one dimension) or vector-valued (for motion in two or three dimensions). At each point in time its value represents the position of an object at that time.
-
Velocity function
This function is the time-derivative of the position function, and gives the velocity of an object at each point in time.
-
Acceleration function
This function is the time-derivative of the velocity function, and the second time-derivative of the position function. It gives the value of the acceleration of an object at each point in time.
-
Time-derivative
The time-derivative of a function is a new function whose value at each point represents the rate of change of the original function with respect to time.
-
Simple harmonic motion
Periodic motion that can be described by special types of position functions. Examples of simple harmonic motion include an object moving in a circle and a ball bouncing up and down on a spring.
Terms
Formulae
| The average velocity for an object with position function x(t) over the time interval (t0, t1). | vavg = 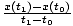 |
| The instantaneous velocity at time t for an object with position function x(t). | v(t) = 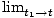 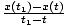 |


 payment page
payment page



