-
Force
A force is defined as a push or a pull.
-
Inertia
The tendency of an object to remain at constant velocity.
-
Inertial reference frame
Any frame in which Newton's Laws are valid.
-
Mass
The amount of matter in a given body.
-
Newton
The name given to a unit of force. One Newton is enough force to cause a 1 KG body to accelerate at a rate of one meter per second per second.
-
Newton's Three Laws
First Law: If
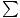 F = 0 then a = 0 and v =constant
F = 0 then a = 0 and v =constant
Second Law: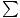 F = ma
F = ma
Third Law: FAB = - FBA
-
Weight
The gravitational force exerted on a given mass.
-
Free Body Diagram
A diagram of all forces acting upon a given object.
-
Normal Force
The force caused by two bodies in direct contact that is perpendicular to the plane of contact.
-
Frictional Force
The force caused by the electrical interaction between two bodies in direct contact that is parallel to the plane of contact and in the opposite direction of the motion of one object relative to the other.
-
Tension Force
The force felt by a rope or cable that transmits another force.
-
Static Frictional Force
The frictional force on two bodies at rest.
-
Coefficient of Static Friction
Defines the proportionality between FN and Fs for two given materials.
-
Kinetic Frictional Force
The frictional force on two bodies in motion relative to one another.
-
Coefficient of Kinetic Friction
Defines the proportionality between FN and Fk for two given materials.
-
Centripetal Acceleration
The acceleration, directed toward the center of a circle, which causes uniform circular motion.
-
Centripetal Force
The force, directed toward the center of a circle, which causes uniform circular motion.
Terms
Formulas
| Newton's Second Law | 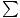 F = ma F = ma |
| Newton's Third Law | FAB = - FBA |
| Formula for maximum static frictional force. | Fsmax = μsFN |
| Formula for kinetic frictional force. | Fk = μkFN |
| Equation for centripetal acceleration. | a = 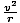 |
| Equation for centripetal force. | F = 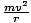 |


 payment page
payment page



