-
Arithmetic Sequence
A sequence in which each term is a constant amount greater or less than the previous term. In this type of sequence, an+1 = an + d, where d is a constant.
-
Common Ratio
In a geometric sequence, the ratio r between each term and the previous term.
-
Convergent Series
A series whose limit as n→∞ is a real number.
-
Divergent Series
A series whose limit as n→∞ is either ∞ or - ∞.
-
Explicit Formula
A formula for the nth term of a sequence of the form an = some function of n.
-
Finite Sequence
A sequence which is defined only for positive integers less than or equal to a certain given integer.
-
Finite Series
A series which is defined only for positive integers less than or equal to a certain given integer.
-
Geometric Sequence
A sequence in which the ratio between each term and the previous term is a constant ratio.
-
Index of Summation
The variable in the subscript of Σ. For
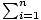 an, i is the
index of summation.
an, i is the
index of summation.
-
Infinite Sequence
A sequence which is defined for all positive integers.
-
Infinite Series
A series which is defined for all positive integers.
-
Recursive Sequence
A sequence in which a general term is defined as a function of one or more of the preceding terms. A sequence is typically defined recursively by giving the first term, and the formula for any term an+1 after the first term.
-
Sequence
A function which is defined for the positive integers.
-
Series
A sequence in which the terms are summed, not just listed.
-
Summation Notation
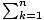 an = a1 + a2 + a3 + a4 + ... + an. The symbol Σ and
its subscript and superscript are the components of summation notation.
an = a1 + a2 + a3 + a4 + ... + an. The symbol Σ and
its subscript and superscript are the components of summation notation.
-
Term
An element in the range of a sequence. A sequence is rarely represented by ordered pairs, but instead by a list of its terms.
Terms
Formulae
| Limit of an Infinite Geometric Series |
For a geometric sequence an = a1rn-1, where -1 < r < 1, the limit
of the infinite geometric series 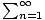 a1rn-1 = a1rn-1 = 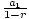 . This is the same as the sum of the infinite geometric
sequence an = a1rn-1. . This is the same as the sum of the infinite geometric
sequence an = a1rn-1.
|
| Sum of a Finite Arithmetic Sequence |
The sum of the first n terms of the arithmetic sequence is Sn = n(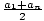 ) or Sn = na1 + ) or Sn = na1 + 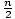 (dn - d ), where d is the
difference between each term. (dn - d ), where d is the
difference between each term.
|
| Sum of a Finite Geometric Sequence |
For a geometric sequence an = a1rn-1, the sum of the first n
terms is Sn = a1(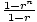 ). ).
|


 payment page
payment page



