-
Axis
The line over which a parabola is symmetric.
-
Branch
The term for each of the two distinct sections of the graph of a hyperbola.
-
Center
For an ellipse and hyperbola, the midpoint between the foci. For a circle, the fixed point from which all points on the circle are equidistant.
-
Circle
The set of all points equidistant from a given fixed point.
-
Conic
The intersection of a plane and a right circular cone.
-
Conjugate Axis
The line segment related to a hyperbola of length 2b whose midpoint is the center.
-
Degenerate Conic
A conic which is not a parabola, ellipse, circle, or hyperbola. These include lines, intersecting lines, and points.
-
Diameter
A line segment that contains the center of a circle whose endpoints are both on the circle, or sometimes, the length of that segment.
-
Directrix
For a parabola, it is the line whose distance from any point on the parabola is the same as the distance from that point to the focus. For a conic defined in polar terms, it is the line whose distance from any point on the conic makes a constant ratio with the distance between that point and the focus.
-
Eccentricity
The ratio
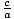 in an ellipse or hyperbola. Under the polar
definition of conics, e is the constant ratio of the distance from a point
to the focus and the distance from that point to the directrix.
in an ellipse or hyperbola. Under the polar
definition of conics, e is the constant ratio of the distance from a point
to the focus and the distance from that point to the directrix.
-
Ellipse
The set of all points such that the sum of the distances from the point to each of two fixed points is constant.
-
Focus
For a parabola, the point whose distance from any point on the parabola is the same as the distance between that point and the directrix. For an ellipse, one of two points--the sum of whose distances to a point on the ellipse is constant. For a hyperbola, one of two points--the difference of whose distances to a point on the hyperbola is constant. Under the polar definition of a conic, it is the point whose distance from a point on the conic makes a constant ratio with the distance between that point and the directrix.
-
Hyperbola
The set of all points such that the difference of the distances between each of two fixed points and any point on the hyperbola is constant.
-
Major Axis
The line segment containing the foci of an ellipse whose endpoints are the vertices whose length is 2a.
-
Minor Axis
The line segment containing the center of an ellipse perpendicular to the major axis whose length is 2b.
-
Parabola
The set of all points such that the distance between a point on the parabola and a fixed line is the same as the distance between a point on the parabola and a fixed point.
-
Radius
A segment between the center of a circle and a point on the circle, or sometimes, the length of that segment.
-
Transverse Axis
The line segment that contains the center and whose endpoints are the two vertices of a hyperbola.
-
Vertex
(Plural = "vertices") For a parabola, the point halfway between the focus and the directrix. For an ellipse, one of two points where the line that contains the foci intersects the ellipse. For a hyperbola, one of two points at which the line containing the foci intersects the hyperbola.
Terms
Formulae
| Polar Form of a Conic | r = 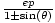 , orr = , orr = 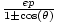 , where
e is the eccentricity of the conic, the
pole is the focus,
and p is the distance between the focus and the directrix. , where
e is the eccentricity of the conic, the
pole is the focus,
and p is the distance between the focus and the directrix.
|
| Standard Form of a Circle | The standard equation for a circle is (x - h)2 + (y - k)2 = r2. The center is at (h, k). The radius is r. |
| Standard Form of an Ellipse |
The standard equation of an ellipse with a horizontal major axis is the
following:
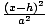 + + 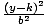 = 1. The center is at
(h, k). The length of the major axis is 2a, and the length of the minor
axis is 2b. The distance between the center and either focus is c,
where c2 = a2 - b2. a > b > 0. The standard equation of an ellipse with
a vertical major axis is the following: = 1. The center is at
(h, k). The length of the major axis is 2a, and the length of the minor
axis is 2b. The distance between the center and either focus is c,
where c2 = a2 - b2. a > b > 0. The standard equation of an ellipse with
a vertical major axis is the following: 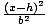 + + 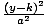 = 1. The center is at (h, k). The length of the major axis is
2a, and the length of the minor axis is 2b. The distance between the center
and either focus is c, where c2 = a2 - b2. a > b > 0. = 1. The center is at (h, k). The length of the major axis is
2a, and the length of the minor axis is 2b. The distance between the center
and either focus is c, where c2 = a2 - b2. a > b > 0.
|
| Standard Form of a Hyperbola |
The standard equation for a hyperbola with a horizontal transverse axis
is 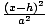 - - 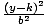 = 1. The center is at
(h, k). The distance between the vertices is 2a. The distance between
the foci is 2c. c2 = a2 + b2. The standard equation for a hyperbola
with a vertical transverse axis is = 1. The center is at
(h, k). The distance between the vertices is 2a. The distance between
the foci is 2c. c2 = a2 + b2. The standard equation for a hyperbola
with a vertical transverse axis is 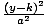 - - 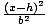 = 1. The center is at (h, k). The distance between the vertices
is 2a. The distance between the foci is 2c. c2 = a2 + b2. = 1. The center is at (h, k). The distance between the vertices
is 2a. The distance between the foci is 2c. c2 = a2 + b2.
|
| Standard Form of a Parabola | If a parabola has a vertical axis, the standard form of the equation of the parabola is this: (x - h)2 = 4p(y - k), where p≠ 0. The vertex of this parabola is at (h, k). The focus is at (h, k + p). The directrix is the line y = k - p. The axis is the line x = h. If a parabola has a horizontal axis, the standard form of the equation of the parabola is this: (y - k)2 = 4p(x - h), where p≠ 0. The vertex of this parabola is at (h, k). The focus is at (h + p, k). The directrix is the line x = h - p. The axis is the line y = k. |


 payment page
payment page



