-
Altitude
See Altitude of a Parallelogram, Altitude of a Trapezoid, Altitude of a Triangle.
-
Altitude of a Parallelogram
In a parallelogram, the segment with one endpoint on a side and perpendicular to that side, with the other endpoint on the line containing the opposite side
-
Altitude of a Trapezoid
In a trapezoid, the segment with one endpoint on a base and perpendicular to that base, with the other endpoint on the line containing the other base.
-
Altitude of a Triangle
In a triangle, the segment with one endpoint on a vertex, and the other endpoint on the side opposite the vertex, and perpendicular to that side.
-
Apothem
A segment with one endpoint at the center of a regular polygon and the other endpoint at the midpoint of a side.
-
Area
A measurement of the combined length and width of two- dimensional regions.
-
Base of a Parallelogram
A side containing the endpoint of an altitude.
-
Center of a Regular Polygon
The point within a regular polygon that is equidistant from all vertices.
-
Central Angle of a Regular Polygon
An angle created whose vertex is at the center and whose sides (rays) extend through the endpoints of a side.
-
Circumference
The length of the curve that defines a circle.
-
Heron's Formula
A formula that determines the area of a triangle. Named after the mathematician who first proved the formula worked, Heron's Formula is useful only if you know the lengths of the sides of a triangle. Heron's Formula states that the area of a triangle is equal to
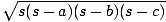 , where s is the
semiperimeter of the triangle, and a, b, and c are the lengths of the three
sides.
, where s is the
semiperimeter of the triangle, and a, b, and c are the lengths of the three
sides.
-
Perimeter
The length of the simple closed curve or curves that define a region.
-
Radius of a Regular Polygon
A segment with one endpoint at the center and the other endpoint at a vertex of a regular polygon.
-
Region
The collection of points that lie within a simple closed curve.
-
Semiperimeter
One-half of the perimeter.
-
Square Unit
A square whose sides are one unit long.
- A = 1/2(bh), where b is the length of the base, and h is the length of the altitude.
- A = Square root [s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)], where s is the semiperimeter and a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides of the triangle.
- A = 1/2((ab)(sin(C)), where a and b are the lengths of two sides and C is their included angle. Circumference C = 2(pi)r, where r is the length of the radius.
Terms
Formulas
| Arc Length | L = (n/360)2(pi)r, where n is the measure of the arc in degrees, and r is the radius of the circle. |
| Area of a Circle | A = (pi * radius)2 |
| Area of a Circle Segment | A = [(n/360)(pi)(radius)2] - [(1/2)bh], where n is the measure of the arc in degrees, b is the measure of the base of the triangle formed by the radii and the chord, and h is the length of the altitude of that triangle. |
| Area of a Parallelogram | A = bh, where b is the length of the base and h is the length of the altitude. |
| Area of a Regular Polygon | A = 1/2(ap), where a is the length of the apothem and p is the perimeter. |
| Area of a Rhombus | A = 1/2(de), where d and e are the lengths of the diagonals. |
| Area of a Sector | A = (n/360)(pi)(radius)2, where n is the measure of the arc in degrees. |
| Area of a Square. | A = s2, where s is the length of a side. |
| Area of a Trapezoid | A = 1/2(h(b1 + b2), where h is the length of the altitude, and b1 and b2) are the lengths of the bases. |
| Area of a Triangle |
|


 payment page
payment page



