-
Alternating Series
A series with terms that alternate signs.
-
Alternating Series Test
An alternating series converges if the absolute values of its terms are decreasing and approach zero.
-
Comparison Test
A series with positive terms converges if there is another series with all terms greater or equal which is known to converge. Similarly, a series with positive terms diverges if there is another series with all terms lesser or equal which diverges.
-
Convergent
The property that the partial sums of a series have a well-defined limit.
-
Absolutely Convergent
The property that the sum of the absolute values of the terms in a series form a convergent series. An absolutely convergent series is automatically convergent.
-
Divergent
A property of a series with partial sums that do not have a well-defined limit.
-
Geometric Series
A series characterized by a constant ratio between consecutive terms.
-
Integral Test
If f (x) is a positive decreasing function, the series fn = f (n) converges if and only if the integral
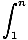 f (x)dx
f (x)dx
tends to a finite limit as n→∞. -
Partial Sum
The sum of finitely many terms from the beginning of a series.
-
Power Series
A series of the form
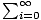 anxn where an is a sequence of real numbers and
x is a variable.
anxn where an is a sequence of real numbers and
x is a variable.
-
Radius of Convergence
A power series
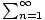 anxn converges absolutely either for all | x| < r, or for
all real numbers x. We then say that the radius of convergence of the power series is r
or ∞, respectively.
anxn converges absolutely either for all | x| < r, or for
all real numbers x. We then say that the radius of convergence of the power series is r
or ∞, respectively.
-
Ratio Test
A method for determining convergence by computing the ratios between consecutive terms of a series. Specifically, if there is a real number 0≤C < 1 such that (an+1/an)≤C for all n > 0, then the series
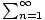 an converges. This is
nothing more than the comparison test applied to a geometric
series.
an converges. This is
nothing more than the comparison test applied to a geometric
series.
-
Series
A sum of the elements in a sequence.
-
Upper Bound
A number which is greater than or equal to all of the partial sums of a sequence.













