-
Antiderivative
An antiderivative of a function f (x) is a function F(x) such that F'(x) = f (x).
-
Definite Integral
The limit approached by the nth upper and lower Riemann sums as n→∞.
-
Integrable
The property that the definite integral of a function exists; that is, the upper and lower Riemann sums converge to the same value as the size of the approximating rectangles shrinks to zero.
-
Riemann Sum
The sum of areas of rectangles approximating the area under the graph of a function; examples include the upper and lower Riemann sums.
-
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
The relationship between differentiation and integration:
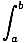 F'(x)dx
F'(x)dx= F(b) - F(a) 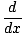
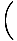
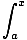 f (t)dt
f (t)dt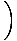
= f (x)
-
Lower Riemann Sum
An approximation to the area below the graph of a function, equal to the total area of a number of thin rectangles inscribed in the region below the graph.
-
Upper Riemann Sum
An approximation to the area below the graph of a function, equal to the total area of a number of thin rectangles containing the region below the graph.
-
Telescoping Limits
The following property of the definite integral:
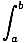 f (x)dx +
f (x)dx + 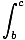 f (x)dx =
f (x)dx = 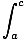 f (x)dx
f (x)dx


 payment page
payment page



