Please wait while we process your payment
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
Please wait while we process your payment

By signing up you agree to our terms and privacy policy.
Don’t have an account? Subscribe now
Create Your Account
Sign up for your FREE 7-day trial
By signing up you agree to our terms and privacy policy.
Already have an account? Log in
Your Email
Choose Your Plan
Individual
Group Discount
Save over 50% with a SparkNotes PLUS Annual Plan!
 payment page
payment page
Purchasing SparkNotes PLUS for a group?
Get Annual Plans at a discount when you buy 2 or more!
Price
$24.99 $18.74 /subscription + tax
Subtotal $37.48 + tax
Save 25% on 2-49 accounts
Save 30% on 50-99 accounts
Want 100 or more? Contact us for a customized plan.
 payment page
payment page
Your Plan
Payment Details
Payment Summary
SparkNotes Plus
You'll be billed after your free trial ends.
7-Day Free Trial
Not Applicable
Renews July 10, 2025 July 3, 2025
Discounts (applied to next billing)
DUE NOW
US $0.00
SNPLUSROCKS20 | 20% Discount
This is not a valid promo code.
Discount Code (one code per order)
SparkNotes PLUS Annual Plan - Group Discount
Qty: 00
SparkNotes Plus subscription is $4.99/month or $24.99/year as selected above. The free trial period is the first 7 days of your subscription. TO CANCEL YOUR SUBSCRIPTION AND AVOID BEING CHARGED, YOU MUST CANCEL BEFORE THE END OF THE FREE TRIAL PERIOD. You may cancel your subscription on your Subscription and Billing page or contact Customer Support at custserv@bn.com. Your subscription will continue automatically once the free trial period is over. Free trial is available to new customers only.
Choose Your Plan
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
For the next 7 days, you'll have access to awesome PLUS stuff like AP English test prep, No Fear Shakespeare translations and audio, a note-taking tool, personalized dashboard, & much more!
You’ve successfully purchased a group discount. Your group members can use the joining link below to redeem their group membership. You'll also receive an email with the link.
Members will be prompted to log in or create an account to redeem their group membership.
Thanks for creating a SparkNotes account! Continue to start your free trial.
We're sorry, we could not create your account. SparkNotes PLUS is not available in your country. See what countries we’re in.
There was an error creating your account. Please check your payment details and try again.
Please wait while we process your payment

Your PLUS subscription has expired
Please wait while we process your payment
Please wait while we process your payment

Conformations of Higher Alkanes
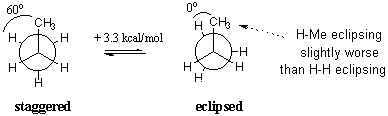
Propane, $C_3 H_8 $, is the next member of the alkane family. Conceptually, propane can be viewed as ethane with one methyl substituent. Instead of analyzing both C-C bonds at the same time, it is more convenient to look at a single C-C and generalize the behavior of the remaining methyl group. The Newman projections show that propane has a set of eclipsed and staggered conformations similar to ethane, but with a torsional strain of 3.3 kcal/mol. Each eclipsed conformation now consists of two eclipsed C-H bonds and one C-H eclipsed with a $C-CH_3 $ bond. We can infer that the latter eclipsing interaction has an energetic "cost" of 1.3 kcal/mol. Bear in mind that these energies do not measure electronic repulsion in any absolute sense, but merely provide figures relative to the more stable staggered state.
Butane, $C_4 H_10 $, has many conformations since its dihedral angles could vary across three C-C bonds. We focus on the central $C_2 –C_3 $ bond and treat the end carbons generally as methyl groups. Conformationally, butane is more complex than ethane or propane. For ethane or propane, the three eclipsed forms are identical in energy, as are the three staggered forms. These structures are degenerate. Such degeneracy is broken in butane, which has two different eclipsed conformations and two different staggered conformations. These conformations differ by the relative positions of the two methyl substituents.
In the most stable conformation, the two methyl groups lie as far apart from each other as possible with a dihedral angle of 180 degrees. This particular staggered conformation is called anti. The other staggered conformation has a Me-Me dihedral angle of 60 degrees and is called gauche. The gauche form is less stable than the anti form by 0.9 kcal/mol due to steric hindrance between the two methyl groups. Such an interaction is often referred to as a gauche-butane interaction because butane is the first alkane discovered to exhibit such an effect.
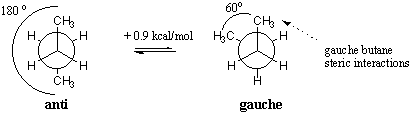
Pentane and higher alkanes have conformational preferences similar to ethane and butane. Each dihedral angle tries to adopt a staggered conformation and each internal C-C bond attempts to take on an anti conformation to minimize the potential energy of the molecule. The most stable conformation of any unbranched alkane follows these rules to take on zigzag shapes:
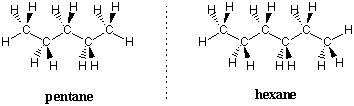
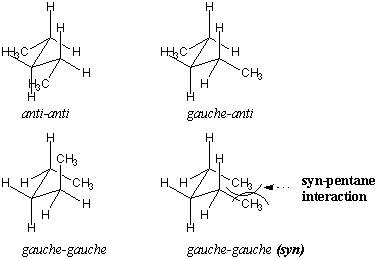
Let's analyze the staggered conformations of pentane in more detail, considering conformations about the $C_2 –C_3 $ and $C_3 –C_4 $ bonds. shows a few possible permutations. The most stable conformation is anti at both bonds, whereas less stable conformations contain gauche interactions. One gauche-gauche conformer is particularly unfavorable because methyl groups are aligned with parallel bonds in close proximity. This conformation is called syn. This type of steric hindrance across five atoms is called a syn-pentane interaction. Syn-pentane interactions have an energetic cost of about 3.6 kcal/mol relative to the anti-anti conformation and are therefore disfavored.
Please wait while we process your payment

