Suggestions
Use up and down arrows to review and enter to select.Please wait while we process your payment
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
Please wait while we process your payment

By signing up you agree to our terms and privacy policy.
Don’t have an account? Subscribe now
Create Your Account
Sign up for your FREE 7-day trial
Already have an account? Log in
Your Email
Choose Your Plan
Individual
Group Discount
Save over 50% with a SparkNotes PLUS Annual Plan!
 payment page
payment page
Purchasing SparkNotes PLUS for a group?
Get Annual Plans at a discount when you buy 2 or more!
Price
$24.99 $18.74 /subscription + tax
Subtotal $37.48 + tax
Save 25% on 2-49 accounts
Save 30% on 50-99 accounts
Want 100 or more? Contact us for a customized plan.
 payment page
payment page
Your Plan
Payment Details
Payment Summary
SparkNotes Plus
You'll be billed after your free trial ends.
7-Day Free Trial
Not Applicable
Renews November 28, 2024 November 21, 2024
Discounts (applied to next billing)
DUE NOW
US $0.00
SNPLUSROCKS20 | 20% Discount
This is not a valid promo code.
Discount Code (one code per order)
SparkNotes PLUS Annual Plan - Group Discount
Qty: 00
SparkNotes Plus subscription is $4.99/month or $24.99/year as selected above. The free trial period is the first 7 days of your subscription. TO CANCEL YOUR SUBSCRIPTION AND AVOID BEING CHARGED, YOU MUST CANCEL BEFORE THE END OF THE FREE TRIAL PERIOD. You may cancel your subscription on your Subscription and Billing page or contact Customer Support at custserv@bn.com. Your subscription will continue automatically once the free trial period is over. Free trial is available to new customers only.
Choose Your Plan
For the next 7 days, you'll have access to awesome PLUS stuff like AP English test prep, No Fear Shakespeare translations and audio, a note-taking tool, personalized dashboard, & much more!
You’ve successfully purchased a group discount. Your group members can use the joining link below to redeem their group membership. You'll also receive an email with the link.
Members will be prompted to log in or create an account to redeem their group membership.
Thanks for creating a SparkNotes account! Continue to start your free trial.
We're sorry, we could not create your account. SparkNotes PLUS is not available in your country. See what countries we’re in.
There was an error creating your account. Please check your payment details and try again.
Please wait while we process your payment

Your PLUS subscription has expired
Please wait while we process your payment
Please wait while we process your payment

Zygomycota: The Conjugation Fungi
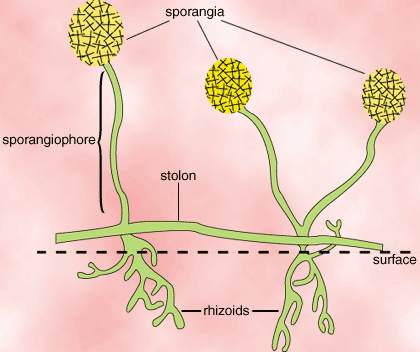
The Zygomycota, or conjugation fungi, include molds, such as those that invade breads and other food products. The identifying characteristics of the Zygomycota are the formation of a zygospore during sexual reproduction and the lack of hyphal cell walls except in reproductive structures. Many (~100 species) are known plant root symbionts.
The mycelia of Zygomycota are divided into three types of hyphae. The rhizoids reach below the surface and function in food absorbtion. Above the surface, sporangiophores bear the spore-producing sporangia. Groups of rhizoids and sporangiophores are connected above the surface by stolons. Cell walls separating individual cells are absent in all but reproductive structures, allowing cytoplasm and even nuclei to move between cells.
Like all fungi, Basidiomycota can undergo both asexual and sexual reproduction. Asexual reproduction in Zygomycota is similar to that in other types of fungi, while sexual reproduction bears some similarity to that in Ascomycota.
Asexual reproduction in Zygomycota varies greatly among orders and species. Spores may be formed by the separation and thickening of hyphal cells. They may also be produced in specialized organs, whose structure is also widely varied.
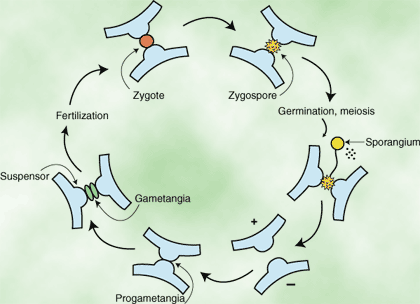
Like Ascomycota, some Zygomycota have two mating types, though individual species may only have one mating type. When hyphae from opposite mating types meet, they produce structures called progametangia that are dense and multinucleate. Cell walls form to separate the tips of the progametangia into gametangia, which continue to be attached to the mating hyphae by the remaining suspensors. Plasmogamy then occurs between the two gametangia to form a zygote. Next, karyogamy takes place within the zygote. The cell walls of the zygote are thin at first, but later thicken into a zygospore. Germination begins when the diploid nucleus undergoes meiosis and a sporangium develops at the end of a germ tube. Spores are produced within the sporangium.
Please wait while we process your payment

