Suggestions
Use up and down arrows to review and enter to select.Please wait while we process your payment
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
Please wait while we process your payment

By signing up you agree to our terms and privacy policy.
Don’t have an account? Subscribe now
Create Your Account
Sign up for your FREE 7-day trial
Already have an account? Log in
Your Email
Choose Your Plan
Individual
Group Discount
Save over 50% with a SparkNotes PLUS Annual Plan!
 payment page
payment page
Purchasing SparkNotes PLUS for a group?
Get Annual Plans at a discount when you buy 2 or more!
Price
$24.99 $18.74 /subscription + tax
Subtotal $37.48 + tax
Save 25% on 2-49 accounts
Save 30% on 50-99 accounts
Want 100 or more? Contact us for a customized plan.
 payment page
payment page
Your Plan
Payment Details
Payment Summary
SparkNotes Plus
You'll be billed after your free trial ends.
7-Day Free Trial
Not Applicable
Renews November 28, 2024 November 21, 2024
Discounts (applied to next billing)
DUE NOW
US $0.00
SNPLUSROCKS20 | 20% Discount
This is not a valid promo code.
Discount Code (one code per order)
SparkNotes PLUS Annual Plan - Group Discount
Qty: 00
SparkNotes Plus subscription is $4.99/month or $24.99/year as selected above. The free trial period is the first 7 days of your subscription. TO CANCEL YOUR SUBSCRIPTION AND AVOID BEING CHARGED, YOU MUST CANCEL BEFORE THE END OF THE FREE TRIAL PERIOD. You may cancel your subscription on your Subscription and Billing page or contact Customer Support at custserv@bn.com. Your subscription will continue automatically once the free trial period is over. Free trial is available to new customers only.
Choose Your Plan
For the next 7 days, you'll have access to awesome PLUS stuff like AP English test prep, No Fear Shakespeare translations and audio, a note-taking tool, personalized dashboard, & much more!
You’ve successfully purchased a group discount. Your group members can use the joining link below to redeem their group membership. You'll also receive an email with the link.
Members will be prompted to log in or create an account to redeem their group membership.
Thanks for creating a SparkNotes account! Continue to start your free trial.
We're sorry, we could not create your account. SparkNotes PLUS is not available in your country. See what countries we’re in.
There was an error creating your account. Please check your payment details and try again.
Please wait while we process your payment

Your PLUS subscription has expired
Please wait while we process your payment
Please wait while we process your payment

Biogeography
The field of biogeography is concerned with the distribution of species in relation both to geography and to other species. Biogeography comprises two disciplines: historical biogeography, which is concerned with the origins and evolutionary histories of species on a long time scale, and ecological biogeography, which deals with the current interactions of species with their environments and each other on a much shorter time scale.
Historical biogeographers depend heavily on evidence from other disciplines. Fossil records provide a large part of the information needed to determine distributions and past interactions. Molecular biology furnished historical biogeographers with molecular clocks, metabolic molecules whose change over time help track the relatedness of species.
Historical biogeographers also make use of a tool called an area cladogram. This diagram is made by taking a taxonomic tree, which shows various species and their relatedness, and replacing the species names with the geographic location in which those species are found. This new tree allows scientists to determine how the differences in environments have effected the evolutionary history of different species of common origin. A sample area cladogram is shown in .
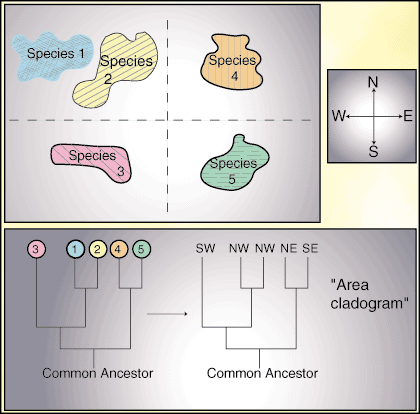
Unlike historical biogeographers, ecological biogeographers make extensive use of current population information. They study the ways in which species develop and interact in the presence of other species and different environments. Many ecological biogeographers mimic Darwin: they study island communities as a type of experimental system to test hypotheses about species development.
Much of ecological biogeography is concerned with species richness, the number of different species an area supports. In specific, ecological biographers have developed the species richness equilibrium model. The model begins with an uninhabited "island" that can be either a literal island or an area of like habitats completely surrounded by unlike habitats. All species available to colonize the new area are called the "species pool." As more and more new species enter the new area, the species pool becomes smaller and smaller, and the immigration rate (the probability that any given species moving into the area will be a new species) decreases. At the same time, the island becomes more and more crowded and supplies become scarce, causing the extinction rate to increase. The point at which the extinction rate and the immigration rate balance is called the equilibrium point. The model predicts that changes in extinction and immigration rates will tend toward the equilibrium point, which is different for every island, depending on resources and degree of separation from other areas. This is shown graphically in the figure below.
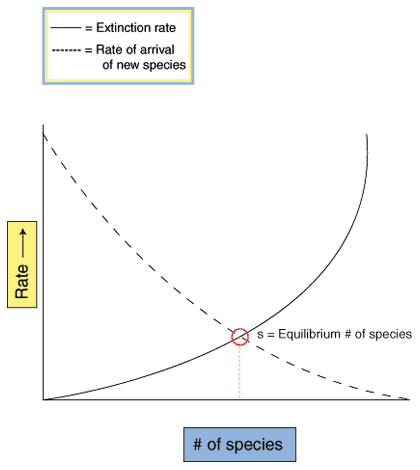
Please wait while we process your payment

