-
Domain
The set of all possible inputs of a function.
-
Function
An operation that assigns a correspondence from elements of one set to elements of another set.
-
Period
The repeating interval of a periodic function; the period of a function is a real number.
-
Periodic Function
A function that repeats itself in regular intervals; it follows this equation: f (x + c) = f (x), where c is a constant.
-
Range
The set of all possible outputs of a function.
-
Reference Angle
The positive acute angle formed between the terminal side of an angle and the x-axis.
-
Rule
The part of a function that dictates the exact correspondence between the elements of one set and the elements of another set.
-
Trigonometric Functions
There are six trigonometric functions: Sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant, and cotangent.
-
Unit Circle
The circle whose center is at the origin and whose radius is one.
Terms
Formulae
| Cosecant |
Given a point P(x, y) on the terminal side of an
angle θ in standard
position, distance d from the
origin, cosecant(θ) = csc(θ) = 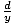 . .
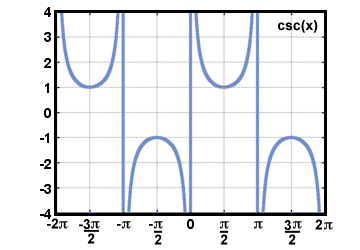 |
| Cosine |
Given a point P(x, y) on the terminal side of an
angle θ in standard
position,
distance d from the origin,
cosine(θ) = cos(θ) = 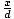 . .
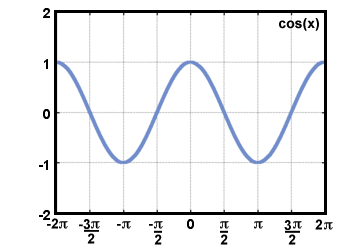 |
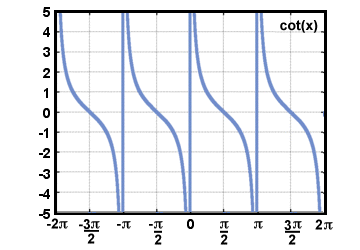
| Cotangent |
Given a point P(x, y) on the terminal side of an
angle θ in standard
position,
cotangent(θ) = cot(θ) = 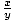 . .
 |
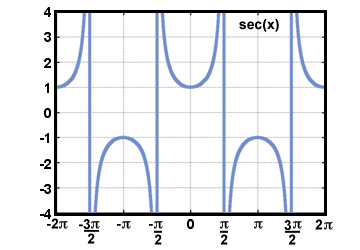
| Secant |
Given a point P(x, y) on the terminal side of an
angle θ in standard
position,
distance d from the origin, secant(θ) = sec(θ) = 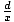 . .
 |
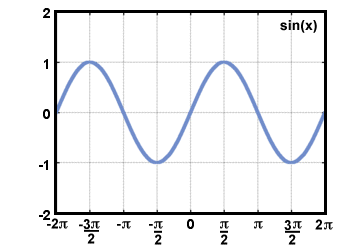
| Sine |
Given a point P(x, y) on the terminal side of an
angle θ in standard
position,
distance d from the origin, sine(θ) = sin(θ) = 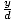 . .
 |
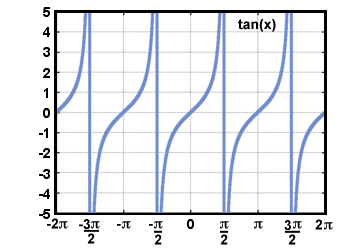
| Tangent |
Given a point P(x, y) on the terminal side of an
angle θ in standard
position,
tangent(θ) = tan(θ) = 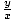 . .
 |


 payment page
payment page



