-
Composition
Given two functions f : S→T and g : T→U, the function gof : S→U defined by applying f and then g is called the composition of g and f.
-
Continuous
A function f is said to be continuous at a pointx0 of its domain if it has a limit there, and that limit agrees with the value f (x0). In mathematical notation:
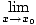 f (x) = f (x0)
f (x) = f (x0)
If the function is continuous at every point of its domain, then one simply says it is continuous. -
Domain
The set of values that a function f takes as its input.
-
Elementary Functions
A standard library of functions including the linear, polynomial, rational, power, and trigonometric functions.
-
Function
A rule f that assigns to each element in a set S a unique element in a set T, which is written f : S→T.
-
Image
The value f (x) which a function f assigns to a particular value x in its domain.
-
Interval
A set consisting of the real numbers between two fixed points, possibly including one or both of these endpoints. An open interval(a, b) is the set of real numbers x such that a < x < b (excluding the endpoints). A closed interval[a, b] is the set of real numbers x such that a≤x≤b (including the endpoints).
-
Invertible
A term that describes a function f : S→T such that there exists a function g : T→S with (gof )(x) = x for each element xâààS.
-
Limit
The value that a function f (x) approaches as x approaches a particular value x0. This is the intuition behind a more rigorous definition.
-
Linear Function
A function of the form f (x) = ax + b, where a and b are real numbers. The graph of such a function is a straight line.
-
Polynomial Function
A function of the form f (x) = anxn + ... + a1x + a0 for real numbers a0,…an.
-
Power Function
A function of the form f (t) = Crt that is used to model exponential growth or decay.
-
Logarithm
The inverse of a power function f (t) = Crt is the logarithm with base r, denoted logr(t).
-
Range
The set within which the output of a function f lies.
-
Rational Function
A function that is formed by taking the quotient of two polynomials.
-
Set
A collection of objects (which are called elements).
-
Slope
The number a for the linear function f (x) = ax + b, indicating the steepness of the graph of f.
-
Trigonometric Function
A periodic function involving sines, cosines, tangents, or their reciprocals or inverses.
-
y-intercept
The number b = f (0) for a linear function f (x) = ax + b, indicating the vertical coordinate of the intersection point of the graph of f with the y-axis.


 payment page
payment page



