-
Dimensions
The number of rows and the number of columns in a matrix. For example, a 3×4-dimensional matrix has 3 rows and 4 columns.
-
Elementary Row Operations
There are three elementary row operations:
- Multiplying a row by a constant.
- Switching two rows.
- Adding a constant times a row to another row.
-
Identity Matrix
The matrix
I = 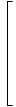
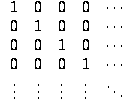
Which, when multiplied by any matrix, does not change the matrix. In other words, any matrix multiplied by I is equal to itself. -
Matrix
A way of representing data in a rectangular array.
A = 

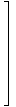
-
Reduced Row-Echelon Form
The form of a matrix in which the first m×m entries form the identity matrix:
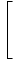

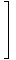
-
Row Reduction
The process through which a matrix is converted to reduced row-echelon form, using elementary row operations.
-
Scalar
A single constant, variable, or expression.













