-
Data Table
A list of x-values and their corresponding y-values.
-
Negative Slope
y always decreases when x increases and y always increases when x decreases.
-
Ordered Pair
A pair of numbers in a specific order. For example, (3, 7) and (8, - 1) are ordered pairs. Two ordered pairs are equivalent if their first members are equal and their second members are equal. However, the order of the two numbers is important; (1, 2) is not equivalent to (2, 1).
-
Origin
The point (0, 0).
-
Parallel Lines
Two lines are parallel if they have the same slope. Parallel lines, when extended, do not intersect at any point.
-
Perpendicular Lines
Two lines are perpendicular if their slopes are opposite reciprocals of each other. Perpendicular lines intersect each other at right angles.
-
Positive Slope
y always increases when x increases, and y always decreases when x decreases.
-
Slope
Given two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) on a line, the slope of the line is equal to:
m = 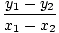
-
x-axis
The horizontal axis of a graph, with which the x-values are plotted.
-
x-coordinate
The number which corresponds to the value of x in an ordered pair.
-
x-intercept
The point at which the graph of a line crosses the x-axis. The point at which y = 0.
-
xy-graph
A two-dimensional way of representing points. x-values are plotted with the horizontal axis, and y-values are plotted with the vertical axis.
xy-graph 
xy-graph -
y-axis
The vertical axis of a graph, with which the y-values are plotted.
-
y-coordinate
The number which corresponds to the value of y in an ordered pair.
-
y-intercept
The point at which the graph of a line crosses the y-axis. The point at which x = 0.













