Suggestions
Use up and down arrows to review and enter to select.Please wait while we process your payment
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
Please wait while we process your payment

By signing up you agree to our terms and privacy policy.
Don’t have an account? Subscribe now
Create Your Account
Sign up for your FREE 7-day trial
Already have an account? Log in
Your Email
Choose Your Plan
Individual
Group Discount
Save over 50% with a SparkNotes PLUS Annual Plan!
 payment page
payment page
Purchasing SparkNotes PLUS for a group?
Get Annual Plans at a discount when you buy 2 or more!
Price
$24.99 $18.74 /subscription + tax
Subtotal $37.48 + tax
Save 25% on 2-49 accounts
Save 30% on 50-99 accounts
Want 100 or more? Contact us for a customized plan.
 payment page
payment page
Your Plan
Payment Details
Payment Summary
SparkNotes Plus
You'll be billed after your free trial ends.
7-Day Free Trial
Not Applicable
Renews November 28, 2024 November 21, 2024
Discounts (applied to next billing)
DUE NOW
US $0.00
SNPLUSROCKS20 | 20% Discount
This is not a valid promo code.
Discount Code (one code per order)
SparkNotes PLUS Annual Plan - Group Discount
Qty: 00
SparkNotes Plus subscription is $4.99/month or $24.99/year as selected above. The free trial period is the first 7 days of your subscription. TO CANCEL YOUR SUBSCRIPTION AND AVOID BEING CHARGED, YOU MUST CANCEL BEFORE THE END OF THE FREE TRIAL PERIOD. You may cancel your subscription on your Subscription and Billing page or contact Customer Support at custserv@bn.com. Your subscription will continue automatically once the free trial period is over. Free trial is available to new customers only.
Choose Your Plan
For the next 7 days, you'll have access to awesome PLUS stuff like AP English test prep, No Fear Shakespeare translations and audio, a note-taking tool, personalized dashboard, & much more!
You’ve successfully purchased a group discount. Your group members can use the joining link below to redeem their group membership. You'll also receive an email with the link.
Members will be prompted to log in or create an account to redeem their group membership.
Thanks for creating a SparkNotes account! Continue to start your free trial.
We're sorry, we could not create your account. SparkNotes PLUS is not available in your country. See what countries we’re in.
There was an error creating your account. Please check your payment details and try again.
Please wait while we process your payment

Your PLUS subscription has expired
Please wait while we process your payment
Please wait while we process your payment

Conformations of Ethane
In the last chapter, we saw that it was possible to describe the complete 3-dimensional shape of methane by specifying its bond angles and bond lengths. Ethane, which is comprised of two methyl groups attached to each other, has properties very similar to those of methane. However, the complete 3-dimensional shape of ethane cannot be specified by these bond lengths and bond angles alone because ethane can internally rotate about its C-C bond.
To understand why ethane has this extra degree of freedom, consider the cylindrically symmetric nature of $\sigma$ bonds. The $\sigma$ bond can maintain a full degree of overlap while its two ends rotate. Hence, the energetic barrier to rotation about sigma bonds is generally very low. Unlike $\pi$ bonds in alkenes, the C-C sigma bond does not hold the two methyl groups in fixed positions relative to one another. The different spatial arrangements formed by rotations about a single bond are called conformations or conformers.
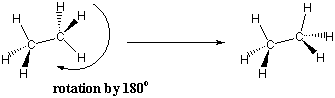
Several methods are used by organic chemists to help them visualize the conformations of molecules. One of these methods uses wedges to denote bonds that are extending out from the plane of the page toward the reader and dashes to indicate bonds that are going into the plane of the page away from the reader. This notation is frequently used to represent the tetrahedral geometry of $sp^3$-hydridized carbons.
A Newman projection can be used to specify the conformation of a particular bond with clarity and detail. A Newman projection represents the head-on look down the bond of interest. The circle in the Newman projection represents the atom in front of the bond, and the lines radiating from the center are the bonds of that atom. The bonds of the rear atom emerge from the sides of the circle.
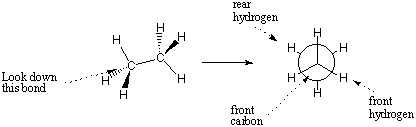
Newman projections can be characterized by the angles formed between bonds on the front atom and bonds on the rear atom. Such angles are called dihedral angles. The full 3D shape of any molecule can be described by its bond lengths, bond angles, and dihedral angles.
While there are an infinite number of conformations about any sigma bond, in ethane two particular conformers are noteworthy and have special names. In the eclipsed conformation, the C-H bonds on the front and back carbons are aligned with each other with dihedral angles of 0 degrees. In the staggered conformation, the C-H bonds on the rear carbon lie between those on the front carbon with dihedral angles of 60 degrees.
Please wait while we process your payment

